QUICK SORT
Quicksort (also known as partition-exchange sort) is an efficient sorting algorithm, which is used for sorting array elements.It is based on divide and conquer algorithm. It is still a commonly used algorithm for sorting. When implemented well, it can be about two or three times faster than heap sort and merge sort. Quicksort first divides a large list into two smaller sub-lists using pivot element and then recursively sort the sub arrays.Best case time complexity : The best case is when the pivot is the median of the array,
and then the left and the right part will have same size.O(n log n)
worst case time complexity: This happens when the pivot is the smallest (or the largest)
element.
Then one of the partitions is empty, and we repeat recursively the procedure for N-1 elements.O(n2)
Average case time complexity: O(n log n)Then one of the partitions is empty, and we repeat recursively the procedure for N-1 elements.O(n2)
Steps to implement Quick sort
- Pick an element, called a pivot, from the array.
- Partitioning: reorder the array so that all elements with values less than the pivot come before the pivot, while all elements with values greater than the pivot come after it (equal values can go either way). After this partitioning, the pivot is in its final position. This is called the partition operation.
- Recursively apply the above steps to the sub-array of elements with smaller values and separately to the sub-array of elements with greater values.
 |
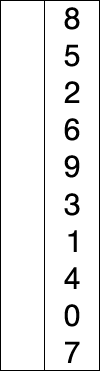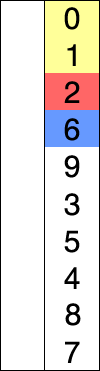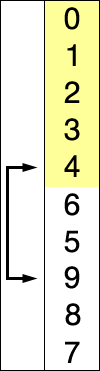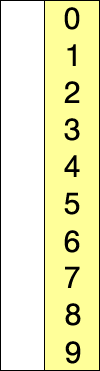
| Quick Sorting |
Quick sort example
import java.util.Scanner;
class SortUsingQuickSort {
private int arr[];
private int length;
public void sort(int[] inputArr) {
if (inputArr == null || inputArr.length == 0) {
return;
}
this.arr = inputArr;
length = inputArr.length;
quickSort(0, length - 1);
}
private void quickSort(int lowerIndex, int higherIndex) {
int i = lowerIndex;
int j = higherIndex;
//taking pivot as middle index number
int pivot = arr[lowerIndex+(higherIndex-lowerIndex)/2];
// Divide into two arrays
while (i <= j) { /* In each iteration, we'll check a number which is greater then the pivot from left side and also we'll check a number which is less then the pivot from right side.*/
while (arr[i] < pivot) {
i++;
}
while (arr[j] > pivot) {
j--;
}
if (i <= j) {
exchangeNumbers(i, j);
//move index to next position on both sides
i++;
j--;
}
}
// call quickSort() method recursively
if (lowerIndex < j)
quickSort(lowerIndex, j);
if (i < higherIndex)
quickSort(i, higherIndex);
}
private void exchangeNumbers(int i, int j) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
public static void main(String a[]){
SortUsingQuickSort sorting = new SortUsingQuickSort();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the size of the array : ");
int size = sc.nextInt();
int[] input = new int[size];
System.out.println("Enter the elements of the array : ");
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){
input[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.print("\n Sorted array : ");
sorting.sort(input);
for(int i:input){
System.out.print(i);
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
}
class SortUsingQuickSort {
private int arr[];
private int length;
public void sort(int[] inputArr) {
if (inputArr == null || inputArr.length == 0) {
return;
}
this.arr = inputArr;
length = inputArr.length;
quickSort(0, length - 1);
}
private void quickSort(int lowerIndex, int higherIndex) {
int i = lowerIndex;
int j = higherIndex;
//taking pivot as middle index number
int pivot = arr[lowerIndex+(higherIndex-lowerIndex)/2];
// Divide into two arrays
while (i <= j) { /* In each iteration, we'll check a number which is greater then the pivot from left side and also we'll check a number which is less then the pivot from right side.*/
while (arr[i] < pivot) {
i++;
}
while (arr[j] > pivot) {
j--;
}
if (i <= j) {
exchangeNumbers(i, j);
//move index to next position on both sides
i++;
j--;
}
}
// call quickSort() method recursively
if (lowerIndex < j)
quickSort(lowerIndex, j);
if (i < higherIndex)
quickSort(i, higherIndex);
}
private void exchangeNumbers(int i, int j) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
public static void main(String a[]){
SortUsingQuickSort sorting = new SortUsingQuickSort();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the size of the array : ");
int size = sc.nextInt();
int[] input = new int[size];
System.out.println("Enter the elements of the array : ");
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){
input[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.print("\n Sorted array : ");
sorting.sort(input);
for(int i:input){
System.out.print(i);
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
}