Selection Sort
 | |
| Selection Sort |
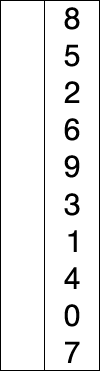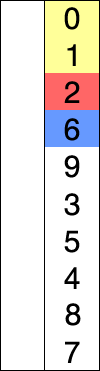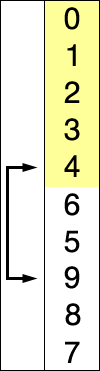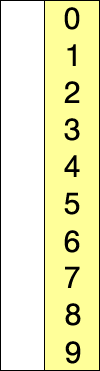
In computer programming, selection sort is a sorting algorithm, which selects an elements and places it to its right place. It is inefficient on large lists, and generally performs worse than the similar insertion sort. Selection sort is popular for its simplicity, and performance
advantages over other complicated algorithms in certain situations.
The algorithm divides the input list into two parts: the sublist of
items already sorted, which is built up from left to right at the front
(left) of the list, and the sublist of items remaining to be sorted that
occupy the rest of the list. Initially, the sorted sublist is empty and
the unsorted sublist is the entire input list. The algorithm proceeds
by finding the smallest (or largest, depending on sorting order) element
in the unsorted sublist, exchanging (swapping) it with the leftmost
unsorted element (putting it in sorted order), and moving the sublist
boundaries one element to the right.
64 25 12 22 11 ► 11 64 25 12 22 ►
11 12 64 25 22 ►
11 12 22 64 25 ►
11 12 22 25 64
Selection Sort Example
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Solution {
public static void doSelectionSort(int[] arr){
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++)
{
int index = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++)
if (arr[j] < arr[index])
index = j;
int smaller = arr[index];
arr[index] = arr[i];
arr[i] = smaller;
}
printArray(arr);
}
public static void printArray(int[] arr){
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Final Sorted array..");
for(int i : arr){
System.out.print(i+", ");
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the size of Array.. ");
int size = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter array elements.. ");
int arr[] = new int[size];
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){
arr[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
Solution.doSelectionSort(arr);
}
}
No comments:
Post a Comment