What is swing?
Swing is a part of JFC (java Foundation Classes) that is used to create GUI application. It is built on the top of AWT and entirely written in java.
Disadvantage of AWT
AWT had some serious shortcomings, To understand Swing, it helps to understand its predecessor, AWT. As its name suggests, AWT is an abstraction. However, people generally expect their application to have a consistent look and feel but AWT is full dependent to platforms, so if the code developed under Windows, then run it on an X Window System or a Macintosh and get more or less the native look and feel on each platform.
Advantage of Swing over AWT
There are many advantages of Swing over AWT, They are as follows
- Swing components are platform independent
- It is lightWeight.
- It supports pluggable look and feel.
- It has more powerful components like tables, lists, scroll panes, color chooser, tabbed pane etc.
- It follows MVC (Model View Controller) architecture.
Frequently used methods present in Component class
- Container getParent()
- String getName()
- void setName(String name)
- void setVisible(boolean visible)
- Color getForeground()
- void setForeground(Color c)
- void setBackground(Color c)
- Color getBackground()
- Dimension getSize()
- void setSize(int width, int height)
- Dimension getPreferredSize()
- void setPreferredSize(Dimension preferredSize)
- Cursor getCursor()
- void setCursor(Cursor cursor)
Container
Containers are integral part of SWING GUI components. A container provides a space where a component can be located.
Following is the list of commonly used containers while designed GUI using SWING.
- JFrame
A JFrame is a window that has a border, title, and supports button components which are used to close or iconify the window. GUI applications uses JFrame.
Example of JFrame by Inheritance
class Test extends JFrame
{
Test() {
setSize(300,300);
setLocation(100,100);
setTitle("hungry4java");
setVisible(true);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); /*to close the JFrame when exit button at top right corner is clicked.*/
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Test();
}
}
JWindow
Like Window, it uses BorderLayout by default. JWindow is the component that can be displayed without being added or attached to another Container. After creating a JWindow, you can call the setVisible() method to display it.
Example of JWindow
public class TopLevelWindows
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
JFrame frame = new JFrame("hungry4java.blogspot.com");
frame.setSize(300,300);
frame.setLocation(100,100);
frame.setVisible(true);
JWindow window = new JWindow();
window.setSize(300,300);
window.setLocation(500,100);
window.setVisible(true);
}
}
JDialog
A JDialog is a window which is used to "talk" to the application. A dialog is used to input data, modify data, change the application settings etc. Dialogs are important means of communication between a user and a computer program.
Example of JDialog
import javax.swing.*;
class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
JFrame frame = new JFrame("hungry4java.blogspot.com");
frame.setSize(300,300);
frame.setLocation(100,100);
frame.setVisible(true);
JWindow window = new JWindow();
window.setSize(300,300);
window.setLocation(500,100);
window.setVisible(true);
JDialog dialog = new JDialog();
dialog.setSize(300,300);
dialog.setLocation(900,100);
dialog.setVisible(true);
}
}
JPanel
A JPanel object is a lightweight (simple) container to hold graphical components, JPanel holds other "normal" graphical components (such as Labels. buttons, etc) and other JPanels.
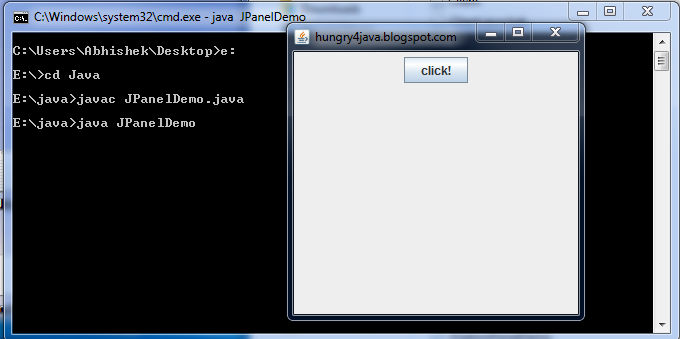
Example of JPanel
import javax.swing.*;
class JPanelDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
JFrame frame = new JFrame("hungry4java.blogspot.com");
frame.setSize(300,300);
frame.setLocation(100,100);
frame.setVisible(true);
JPanel panel = new JPanel();
frame.add(panel);
JButton button = new JButton("click!");
panel.add(button);
}
}
class JPanelDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
JFrame frame = new JFrame("hungry4java.blogspot.com");
frame.setSize(300,300);
frame.setLocation(100,100);
frame.setVisible(true);
JPanel panel = new JPanel();
frame.add(panel);
JButton button = new JButton("click!");
panel.add(button);
}
}
JApplet
JApplet is a container which contains any swing components, that can runs in web browser.
- To compile write "C:\Users\Abhishek\Desktop>FileName.java"
- And to run your JApplet write "C:\Users\Abhishek\Desktop>appletViewer FileName.java
Example of JApplet
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class Test extends JApplet
{
public void paint(Graphics g)
{
g.drawString("Hello..welcome to hungry4java.blogspot.com",150,150);
}
}
/*
<applet code=Test.class width=300 height=300
</applet>
*/



No comments:
Post a Comment